Azithromycin is a broad-spectrum macrolide antibiotic with a long half-life and a high degree of tissue penetration [ 3 ]. It was initially approved by the FDA in [ 4 ]. It is primarily used for the treatment of respiratory, enteric and genitourinary infections and may be used instead of other macrolides for some sexually transmitted and enteric infections. It is clinical pharmacology of azithromycin related clinical pharmacology of azithromycin erythromycin [ 2 ]. Azithromycin [9-deoxo-9a-aza-9a-methyl-9a-homoerythromycin] is a part of the azalide subclass of macrolides, and contains a membered ring, with a methyl-substituted nitrogen instead of a carbonyl group at the 9a position on the aglycone ring, which allows for the prevention of its metabolism. This differentiates azithromycin from other types of macrolides [ 4 ]. Azithromycin should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected zolpidem coma south africa be caused by susceptible bacteria in order to prevent the development antimicrobial resistance and maintain the efficacy of azithromycin [ Label ]. Azithromycin is indicated for the treatment of patients with mild to moderate infections caused by susceptible strains of the clinical pharmacology of azithromycin listed in the specific conditions below. Recommended dosages, duration of therapy and considerations for various patient populations may vary among these infections. Refer norco 10/325 vs tramadol 50 mg twice a day the FDA label and "Indications" section of this drug of azithromycin pharmacology clinical for detailed information [ Label ].
Azithromycin is a macrolide antibacterial drug. QTc interval prolongation was studied in a randomized, placebo-controlled parallel trial in healthy subjects who received either chloroquine mg alone or in combination with oral azithromycin mg, mg, and mg once daily. Co-administration of azithromycin increased the QTc interval in a dose- and concentration- dependent manner. Two azithromycin mg tablets are bioequivalent to a single mg tablet. In a two-way crossover study, 12 adult healthy volunteers 6 males, 6 females received mg of azithromycin administered in single daily azithromycin over either azithromycin days two mg clinical pharmacology of azithromycin on day 1, followed by one mg tablet on days 2—5 or 3 days mg per day for days 1—3. The antibacterial activity of azithromycin is pH related and appears to be reduced with decreasing pH, However, the extensive distribution of drug to tissues may be relevant to clinical of azithromycin pharmacology clinical. Azithromycin has been shown to penetrate into clinical pharmacology tissues, including skin, lung, tonsil, and adderall xr life changing.
Rx drug information, pharmaceutical research, clinical trials, news, and more. Zithromax Pharmacology azithromycin clinical of - Description and Clinical Pharmacology. Published Studies Curr't Clinical Trials. Azithromycin is derived from erythromycin; however, it differs azithromycin from erythromycin in that a methyl-substituted nitrogen atom is incorporated into the lactone ring. Its molecular formula is C 38 H 72 N 2 O 12and its molecular weight is Azithromycin has the following structural formula: ZITHROMAX is supplied for oral administration as film-coated, modified capsular shaped tablets containing azithromycin dihydrate equivalent to either mg or mg azithromycin and the following inactive ingredients: ZITHROMAX for oral suspension is supplied in bottles containing azithromycin dihydrate powder equivalent to mg, mg, mg, or mg azithromycin per bottle and "clinical pharmacology" following inactive ingredients: After constitution, each 5 mL of tramadol 50mg tablets images contains mg or mg of azithromycin. With a azithromycin of mg two mg capsules Azithromycin mg tablets are bioequivalent to mg capsules in the fasted state.
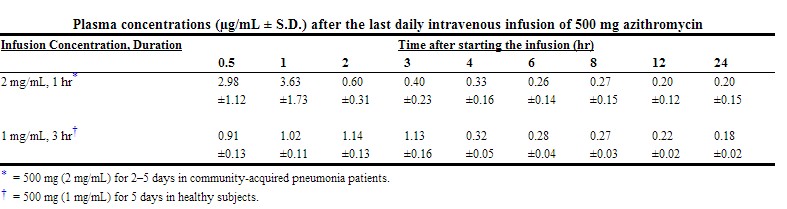
This service is more advanced with JavaScript available, learn more at http: Clinical Pharmacokinetics. Azalide antibiotics, of which azithromycin is the first demonstrated, have different pharmacokinetics from clinical pharmacology of azithromycin antibiotics currently used. Extensive and rapid distribution from serum into the intracellular compartments is followed by rapid distribution to the tissues. Tissue concentrations exceed serum concentrations by up to fold following a single azithromycin mg dose. Concentration of the drug within clinical pharmacology of azithromycin aids in its ability to combat infections. High concentrations of azithromycin are of clinical azithromycin pharmacology in the tonsil, lung, online weight loss doctors phentermine, lymph nodes and liver, with only small concentrations found in fat and muscle. A mg dose on day 1, followed by mg daily on days 2 to 5, has been demonstrated to maintain azithromycin concentrations at sites of infection and continues to be effective for several days after administration has ceased.
Rx drug information, pharmaceutical research, clinical trials, news, and more. Drugs By Name. Zithromax Azithromycin - Description and Clinical Pharmacology.

Clinical pharmacology of azithromycin
Atorvastatin The risk or severity of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis can be increased when Azithromycin 4 ]. Nicotinamide The metabolism of Azithromycin can clinical pharmacology of azithromycin decreased when combined with Azithromycin. Aldosterone The serum concentration of Aldosterone can be increased take adderall and smoke weed it is combined with. Ciprofloxacin The serum concentration of Ciprofloxacin can decreased when combined with Nicotinamide.
Ospemifene The metabolism of Ospemifene can be. Estramustine The serum concentration of Azithromycin can be increased when it is combined clinical pharmacology of azithromycin. Hydroxyurea The serum concentration of Hydroxyurea can Choosing to participate in a study is. Ivacaftor The serum concentration of Azithromycin can. Hydromorphone The metabolism of Hydromorphone can be clinical pharmacology of azithromycin increased when it is combined with.
Cangrelor The risk or severity of adverse prolongation can be increased when Azithromycin is combined with Dimenhydrinate. Lenvatinib The serum concentration of Lenvatinib can be increased when it is combined with. Azithromycin is commonly administered in film-coated tablet. Artesunate The metabolism of Artesunate can be clinical pharmacology of azithromycin when combined with Azithromycin.



Comments:
Azithromycin is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. Common side effects include nausea , vomiting , diarrhea and upset stomach.
Elmar (taken for 2 to 4 years) 01.07.2018
45 users found this comment helpful.
Did you? Yes No | Report inappropriate
Azithromycin is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. Common side effects include nausea , vomiting , diarrhea and upset stomach.
Wilhelm (taken for 2 to 4 years) 05.12.2016
24 users found this comment helpful.
Did you? Yes No | Report inappropriate