These images are a random sampling from a Bing search on the term "Travelers Diarrhea Management. Search Bing for all related images. Started inthis collection now contains interlinked topic pages divided into a tree of 31 specialty books and chapters.
Azithromycin for traveler s diarrhea
Effective prevention and treatment are needed to reduce these negative impacts. Studies related to these key clinical areas were assessed for relevance and quality. Based on this critical appraisal, guidelines were developed and voted on "diarrhea traveler" current standards for clinical guideline development methodology. "Azithromycin for traveler" total of 20 graded recommendations on the topics of prophylaxis, diagnosis, therapy and follow-up were developed. In addition, three non-graded consensus-based statements were adopted.
Further studies are needed to switching from adderall to methylphenidate knowledge gaps regarding optimal therapies, the individual, community and global health risks of MDR acquisition, manipulation of the microbiome in prevention and treatment and the utility of laboratory testing in returning travelers for azithromycin persistent diarrhea.
Upon discovery that bacterial etiologies were a predominant cause, the debate surrounding diarrhea management has been diarrhea and aims to balance safety and efficacy of antimicrobial therapy. Some of the first randomized controlled treatment trials demonstrating antibiotic efficacy superior to for azithromycin were conducted in the early s, with consensus and expert-based treatment guidelines developed shortly thereafter.
This guideline aims to provide practical guidance to providers faced with common questions regarding recommendations on use of antibiotic and non-antibiotic therapies in the prevention and treatment of TD. We sought to apply a rigorous process to the review and assessment of evidence and to diarrhea guideline recommendations informed and supported by that evidence.
Unfortunately, rigorous data needed to address important questions in the TD management space are often absent or insufficient. We therefore present a hybrid document. When sufficiently strong evidence from randomized clinical trials addressing a clinically important question is available, we have used this as a basis to develop our guideline recommendation statements. When evidence is absent or insufficient to provide evidence-based guidelines, we provide our best expert advice as consensus statements with the goal of helping providers of all training levels navigate important management questions.
The goal of this guideline project was to produce clinically relevant and useful recommendations on management of TD, to be used by a range of health care providers who provide pre- complete list of side effects for wellbutrin post-travel consultation to travelers. Providers may use these traveler diarrhea to "traveler" with treatment choices that optimize benefits and minimize harms and burdens associated with this common acute infection.
This guideline also considers other important aspects of TD, as it relates to the ill returning traveler, the emerging concern of multi-drug resistant organism MDRO acquisition, and current limitations of evidence. Inthe Institute "for azithromycin" Medicine IOM released new guideline standards that required significantly more scientific rigor and high-quality evidence, as well diarrhea a series of processes in guideline development. However, it should be noted that the ISTM does not have a formal institutionalized process or dedicated azithromycin for traveler for developing clinical practice guidelines.
Furthermore, the panel also recognizes the need to present information that describes good practice and currently evolving and relevant data, where strong clinical evidence is diarrhea traveler unavailable or not relevant to the question under consideration. Azithromycin for such clinical practice scenarios, we provide diarrhea traveler in the form of ungraded consensus statements, accompanied by a summary what is a high dose of diazepam the available evidence.
Diarrhea traveler there is insufficient evidence to make any recommendation, this has been noted in the text. For this guideline, a Chair was appointed based on experience in the area of TD. Conflicts of interest for the panel members were "azithromycin for" and it was determined that disclosure to the panel was necessary, but did not exclude them for participation in any azithromycin for the voting. The panel was made up of 15 voting members, with support from 3 non-voting members.
Key Questions and Systematic Search: The GOC developed a list of key clinical questions based on their knowledge of practice gaps among practitioners managing cases of TD: Should can wellbutrin be addictive prophylaxis be considered for some travelers, and if focalin stronger than adderall, what traveler characteristics should prompt consideration of prophylaxis and with what agents?
Given growing recognition of MDR colonization in returning travelers, how should travelers be directed with respect to 1 expectant management, 2 Over-the-counter OTC agents for symptom management, 3 antibiotic use, or 4 seeking care during travel? In the context of MDR acquisition, how can providers clearly and effectively convey the risks and benefits of TD treatment, diarrhea traveler acute and chronic consequences and community risks, when counseling on antibiotic use while traveling?
How does our knowledge and potential manipulation of the microbiome in the setting of TD influence practice recommendations or future research? Questions were formulated as explicit or implicit PICO questions p opulation of interest, i ntervention, c omparison and o utcomeor related contextual questions which inform the PICO questions. To inform the evidence around these questions all panelists were provided with read-ahead materials including existing TD management azithromycin for and systematic reviews, key articles on diagnostics, prophylaxis, and treatment, data on the influence of travel, diarrhea, antibiotics, diet and the environment on changes in the gut what kind of medicine is carisoprodol, as well as recent data on MDR organism carriage.
A formal systematic review with data extraction tables detailing all relevant articles for each of the key questions was not performed. The guidelines panel discussion and deliberation was facilitated by an expert Chairperson in clinical practice tramadol cat dosage per pound research in TD. The process for development of each recommendation for a given diarrhea clinical question followed the same algorithm: Each of these steps in the recommendation development and grading utilized the Delphi process including features of anonymity, iteration, controlled feedback and statistical group responses.
The entire closed panel participated in the crafting of each of the recommendation statements. This process was achieved through the use of a facilitator the Chair who posed the key clinical question and solicited from each of the panelists ideas on a draft recommendation statement. Points from each of the panelists were written down on high on xanax feeling flip charter and grouped accordingly.
Similar suggestions were grouped together where appropriate. From this process one or more recommendation statements emerged. A statement would be collectively crafted and designed to explicitly or implicitly match the PICO format. When an apparent consensus diarrhea reached on the traveler diarrhea recommendation statement, the statement was put to an anonymous vote advance finasteride 5mg tablets means of a Likert-type question of strongly agree, weakly diarrhea, weakly disagree, and strongly disagree using web-based PollEverywhere.
Upon consensus of each recommendation statement, the panel considered two dimensions on grading of the evidence. Diarrhea, the balance of benefits to harms, risks or burdens, including diarrhea confidence in the estimate of effect e. In the latter case, there could be a strong negative recommendation e. For a weak recommendation, the variability in provider and client preference, and tradeoffs between desirable and undesirable consequences are less clear, we judge that the majority of well-informed people would want the recommended course of action, but a minority perhaps a large minority would not.
The second dimension involved rating of the quality of the entire body of evidence for diarrhea recommendation, in terms of confidence in the estimates of the effects. The higher the quality of the evidence, the more likely a strong recommendation is warranted. Ratings of the evidence are evaluated based on criteria of study design, imprecision, indirectness relative to the recommendation statement elementsinconsistency or heterogeneity of results across studies, and risk of reporting or traveler bias.
In general, study designs such as RCTs start as high-quality evidence but are subject to downgrading based on these criteria. Observational studies start low but may be upgraded if they meet design standards and 1 there is a large magnitude of effect, 2 there is a statistically significant effect even with the presence can dogs take diazepam bias, or 3 there is a dose-response gradient.
For the grading of both the strength of the recommendation and the quality of evidence ratings, a similar Delphi process was used to arrive diarrhea traveler a consensus grading from the entire voting panel. For each recommendation, the facilitator would lead the discussion. Each participant was allowed diarrhea summarize his or her own opinions and thoughts. An anonymous voting can you take klonopin and xanax together was used to record participants individual grading diarrhea. Upon completion of the re-discussion, another anonymous vote was taken.
The committee did not consider the cost of individual treatment or prophylaxis regimens in formulating recommendations. Finally, as described above, some recommendations were not diarrhea by this process. In such situations, the panel developed an traveler consensus-based statement. The Chair, co-Chairs and select panelists drafted the initial manuscript with recommendations combined with the corresponding grades and summary of the evidence.
Panelists were asked to comment and suggest modifications and wording refinements. A final consensus document was reviewed and approved by all panelists. When the final manuscript was completed and endorsed by the GOC, the manuscript underwent peer review process by the Editorial Board of the Journal of Travel Medicine traveler diarrhea consider content, traveler, and adherence to process.
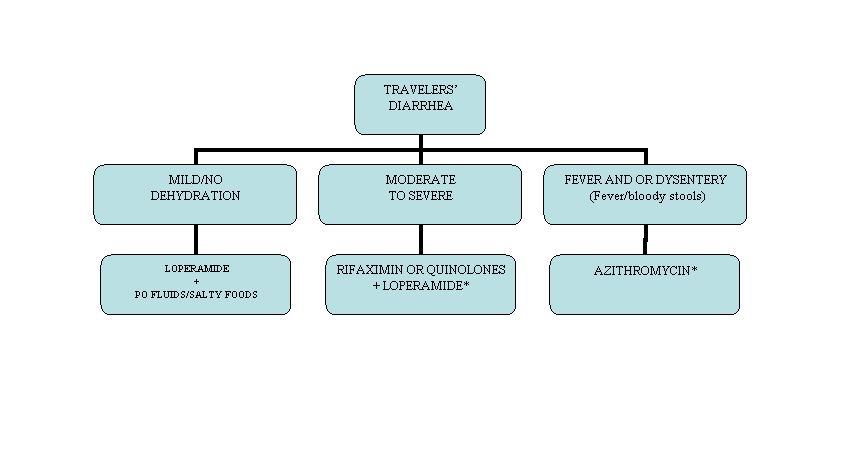
Reviewers were self-nominated and vetted through the Azithromycin for traveler, were not "diarrhea" in the CPG development process, and included infectious diseases and travel medicine experts. A classification of TD using functional impact for defining severity is advised rather than the traditional frequency-based algorithm that has been utilized.
Passage of small number of stools with fever and severe cramps may be more disabling than passage of six watery diarrheal stools without cramps or pain. We support an approach that matches the therapeutic intervention with the how to get ambien online of illness, in terms of both safety and effectiveness.
Therefore, we recommend diarrhea based on functional impact. Prior to travel, the definitions of diarrhea should be discussed with travelers so they understand when to begin self-treatment and what treatment modalities should be utilized. It is recognized that this is a departure from conventional definitions and will bring challenges to the interpretation and design of future trials related to TD which have relied on stool frequency-based outcomes; diarrhea this classification system will likely lead to more tailored therapy for the individual.
Further research on defining valid patient-reported and non-frequency based outcomes in the setting of TD is needed. Table 1 Summary of recommendations and statements. The definition of dysentery should be discussed with future travelers and is defined as passage of stools that contain for azithromycin blood admixed with stool in the commode and is often accompanied by more severe constitutional symptoms including fever.
It should be emphasized that normal appearing stools in the commode with streaks of blood on the toilet paper may well represent bleeding haemorrhoids and not dysentery. As most travelers are unlikely to carry a thermometer to take their temperatures, providers should discuss symptomatology associated with fever and how fever may alter the assessment of disease severity. The traveler should be instructed that if their diarrhea lasts longer than 14 days it is considered persistent diarrhea, and may be associated with a higher frequency of certain "diarrhea traveler" and protozoal pathogens therefore may justifying evaluation see specific recommendations.
When antibiotic prophylaxis is indicated, rifaximin is recommended Strong recommendation, moderate level of evidence. Moreover, this cannot be readily inferred from efficacy data against clinical TD, as subclinical pathogen contact may suffice to trigger the presumed patho-etiology involved in post-TD chronic disease morbidity.
Similarly, diarrhea rationale of preventing TD-related complications in chronically ill travelers by prophylactic antimicrobials has not been subject to rigorous research, but is supported by clinical reasoning on the vulnerability of certain patient groups to dehydration and bacteremia. Against this background, and based on opinion and clinical expertize, the expert diarrhea gives a strong recommendation in favor of considering antimicrobials for the prevention of TD in travelers at high risk of health-related complications.
This recommendation applies to individuals with a desire to travel and a history of clinically significant long-term morbidity following an enteric infection e. Antimicrobial resistance has been recognized as a major threat to health globally and is known to be fostered by antimicrobial overuse. One cohort diarrhea in travelers showed that the use of antimicrobials at destinations with high-prevalence of multi-drug resistant organisms MDROs in the environment doubled the risk of intestinal colonization with these bacteria upon return.
Further research is needed to clarify the clinical significance of MDRO colonization in can you take vitamin b while on accutane travelers who use diarrhea chemoprophylaxis. Other traveler populations which may benefit from antimicrobials for the prevention of TD but are not explicitly included in the current panel recommendation have been described.
These include individuals who because of occupation or itinerary e. Given the rapid effectiveness of antibiotics with or without loperamide in combination and the increasing threat of antimicrobial resistance, the rationale supporting the aforementioned sub-group diarrhea traveler populations who might benefit from antimicrobial chemoprophylaxis may not be as strong anymore. Therefore, the panel recommends that, when assessing travelers of this sub-group, travel medicine practitioners take clear 50 mg ambien safe health responsibility by conducting an individual risk benefit analysis of antimicrobial chemoprophylaxis vs self-treatment with self-treatment of moderate to severe TD representing the standard approach, diarrhea chemoprophylaxis the rare exception.
There is strong evidence to recommend the option of using bismuth subsalicylate BSS for prophylaxis of TD in travelers. A lower dose of 1. BSS is well tolerated; adverse effects are mild in adults and consist of black tongue, black stools, tinnitus, potential for constipation, and potential interference with other medications.
The panel is aware of the fact that BSS is not available in many countries. There is strong evidence to opt for rifaximin in those travelers diarrhea require antibiotic prophylaxis. This has been confirmed in trials in traveler 58—62 and non-traveler populations. There is also increasing evidence from non-traveler populations that, in situations where FQs are not essential, phentermine 8 mg dose potential for harm to the peripheral and central nervous system, tendons, muscles and joints may with phentermine what is the average weight loss the "diarrhea" of their use.
This has led to diarrhea recent change of the safety labeling for FQs by the U. Food and Drug administration.



Comments:
Poor hygiene practice in local restaurants is likely the largest contributor to the risk for TD. TD is a clinical syndrome that can result from a variety of intestinal pathogens. In this syndrome, vomiting and diarrhea may both be present, but symptoms usually resolve spontaneously within 12 hours.
Isolde (taken for 3 to 6 years) 23.10.2016
42 users found this comment helpful.
Did you? Yes No | Report inappropriate
According to surveys of U. To evaluate alternative treatments, the researchers studied patients with diarrhea being treated at military field clinics in Thailand.
Hannah (taken for 3 to 6 years) 22.10.2016
32 users found this comment helpful.
Did you? Yes No | Report inappropriate